The flow of charge carriers, which is due to the applied voltage or electric field is called drift current. In a semiconductor, there are two type of charge carriers, they are called electrons and holes. When the voltage is applied to a semiconductor, the free electrons move towards the +ve terminal of a battery and holes moves towards the –ve terminal of a battery.
Electrons are the negatively charge particle and holes are the positively charged particle. As we know that same charge repel and unlike charge attract each other. Hence, the electrons –ve charge particle are attracted toward the –ve terminal and holes are attracted toward the –ve terminal of the battery.
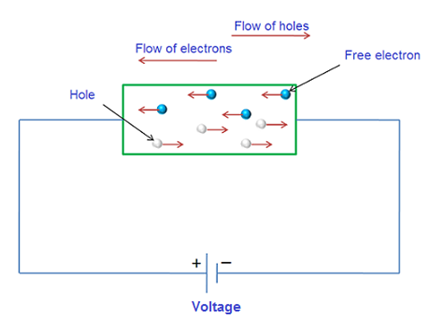
In a semiconductor, the electrons always try to move in a straight line towards the +ve terminal of the battery. But, due to continuous collision with the atoms they change the direction of flow. Each time the electrons strikes an atom it bounce back in a random direction. The applied voltage does not stop the collision and random movement of electrons, but it cause the electrons to drift towards the +ve terminal of the battery.
“The current generated because of the application of external voltage that results in the movement of charge carriers is defined as Drift current.
The main reason behind the occurrence of this current is because of the application of external forces it can be either electric field or voltages”
The average velocity that an electrons or hole achieved due to the applied voltage or electrical field is called drift velocity.
The drift velocity of electrons is given by
Vn = µn E
The drift velocity of holes is given by
Vp = µp E
Where
- Vn -drift velocity of electrons
- Vp -drift velocity of holes
- µn -mobility of electrons
- µp -mobility of holes
- E -applied voltage.
The drift density due to free electrons is given by
Jn = eŋµn E
And the drift current density due to holes given by
Jp = epµp E
Where ,
- Jn – drift current density due to electrons
- Jp –drift current density due to holes
- e –charge of an electron = 1.062×10-19 C.
- ŋ – number of electrons
- p – number holes
Then the total drift current density is
J = Jn + JP
= eŋµn E + epµp E
J = e (ŋµn + pµp ) E.