A Danish physicist named Neil Bohr in 1913 proposed the Bohr atomic model. He modified the problems and limitations associated with Rutherford’s model of an atom.
Earlier in Rutherford Model, Rutherford’s explained in atoms nucleus is positively charged and is surrounded by electrons (negatively charged particles).
According to Bohr Atomic model, a small positively charged nucleus is surrounded by revolving negatively charged electrons in fixed orbits. He concluded that electron will have more energy if it is located away from the nucleus whereas the electrons will have less energy if it located near the nucleus.
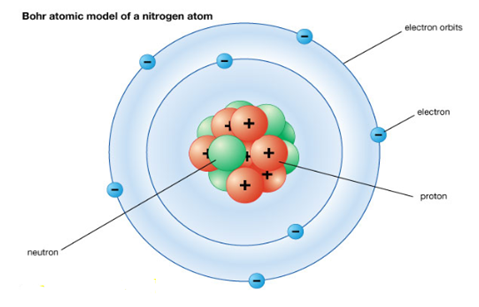
Postulates of Bohr atomic model:
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed circular path termed “orbits” or “shells” or “energy level”.
The orbits are termed as “stationary orbit”.
Every circular orbit has a certain amount of fixed energy and these circular orbits were termed orbital shells. The electron will not radiate energy as long as they continue to revolve around the nucleus in fixed orbital shells.
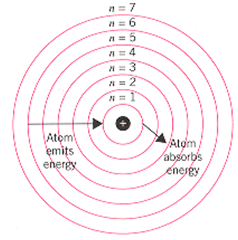
The different energy are denoted by integers such as n=1 or n=2 or n=3 and so on. These are called as quantum numbers. The range of quantum number may vary and begin from the lowest energy level (nucleus side n=1) to highest energy level.
The different energy level or orbits are represented in two way such 1,2,3,4 …… or K, L, M, N……. shells. The lowest energy level of the electron is called ground state.
The change in energy occurs when the electron jump from one energy level to others. In an atom, the electrons are move from lower to higher energy level by acquiring the required energy. However, when an electron loses energy it moves from higher to lower energy level.
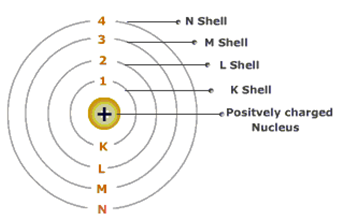
1st orbit (energy level) is represented as K shell and ot can hold upto 2 electrons.
2nd orbit (energy level) is represented as L shell and it can hols up to 8 elctrons.
3rd orbit (energy level) is represented as M shell and it can holes up to 18 electrons. 4th orbit (energy level) is represented as N shell and it can holes up to 32 electrons.
Distribution of Electrons in Orbits or shells:
Electrons are distributed of various orbits or different energy levels can be calculated by formula 2n2. Here “n” represent number of orbits.
The number of electrons in K shell (1st orbit) can be calculated by 2n=2 x 1 = 2. Thus, maximum number of electrons in 1st orbit =2.
Similarly, the number of electrons in L shell (2nd orbit) = 2×2=8. This maximum number of electrons in 2nd orbit=8.
We can use the same formula and can calculate the maximum number of electrons in other shells.